RV JOURNAL OF NURSING SCIENCES (RVJNS)
Volume 4 | Isuue 4 | OCTOBER-DECEMBER 2025 | Pages: 41-47
Original Article
A study to evaluate the Effectiveness of Memory Enhancement Technique on Memory Retention among Nursing Students at Selected College of Bangalore.
Isha Maria Jose1, Daphishongdor Marwein2, Swetha S3, Piyali Biswas4, Sumi Thankachan5, Abin Geogre6, Mrs. Shashwati Sur7
Article history:
Received 05 June 2025
Received in revised form 30 August 2025
Accepted 15 September 2025
Available online 10 October 2025
Corresponding Author
Email: isha2003maria@gmail.com



How to Cite
Jose IM, Marwein D, Swetha S, Biswas P, Thankachan S, George A, Sur S. A study to evaluate the effectiveness of memory enhancement technique on memory retention. RV Journal of Nursing Sciences. 2025;4(4):41–47.
Copyright (c)
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
ABSTRACT
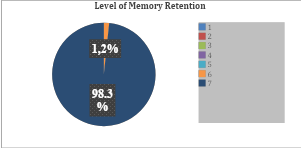
Memory is the mind’s ability to encode, retain, and retrieve information—an indispensable foundation for learning. Memory plays a vital role in the academic and professional life of nursing students. However, one of the most commonly cited challenges among students is the difficulty in retaining large amounts of academic material, primarily due to a lack of formal training in effective memory and recall strategies. This quasi-experimental study evaluated the impact of Memory Enhancement Techniques (METs), particularly mnemonics, on memory retention among 60 first-semester B.Sc. nursing students in Bangalore. Memory retention was assessed using the Multi factorial Memory Questionnaire before and after administering a structured mnemonic exercise. Initially, only 10% of students demonstrated good memory strategies, while 47% showed poor strategies. After the intervention, 62% exhibited good memory strategies, and only 2% had poor strategies. Statistical analysis revealed a significant improvement in memory retention post-intervention (p = 0.000). These results suggest that mnemonics are an effective method for enhancing memory retention in nursing students. The study highlights the importance of incorporating METs into nursing education to improve students’ academic performance and learning outcomes.
References
- Schacter DL, Gilbert DT, Wegner DM, Nock MK. Psychology. 5th Ed. New York: Worth Publishers; 2020.
- Sujatha CC. An investigative study on the level of awareness of memory among secondary school students. IJCRT. 2022;10(4):278-84
- Kirschner PA, Sweller J, Clark RE. Why minimal guidance during instruction does not work: an analysis of the failure of constructivist, discovery, problem-based, experiential, and inquiry-based teaching. Educ Psychol. 2006;41(2):75-86
- Akpan J, Notar CE, Beard L. The impact of mnemonics as an instructional tool. Journal of Education and Human Development. 2021;10(3):20-28.
- Seay S, McAlum E. Mnemonics: principles of organization, attention, association and visualization in memory improvement. Int Educ Psychol J. 2019;5(2):45–52.
- Melo CKC, Roseno AVS, Silva AJL, Pessoa TF, Santana GA, Santiago LES, Montenegro DLF, Almeida LN, Lima ILB. Memory self-assessment of university students (Autoavaliação da memória de jovens universitários). Audiol Commun Res. 2021;26:e2468.
- Ali LAEH, Ali MIEB, Ali SMA, Nashwan AJ. Smartphone dependency, digital amnesia, and somatic symptoms among nursing students: the challenge of artificial intelligence. BMC Nurs. 2025;24:599. doi:10.1186/s12912-025-03228.
- Times of India. 40% medical students experienced forgetfulness linked to smartphone use: Study. Times of India. 2023 [cited 2025 Oct 10]. Available from:
- Subramanian P, Renuka K. Effectiveness of memory-enhancement technique on memory retention among B.Sc. Nursing students at selected nursing college, Puducherry. J Educ Health Promot. 2021;10:455. doi:10.4103/jehp.jehp_1291_20.
- Kaur P. Effect of mnemonics learning technique on memory: an experimental study among B.Sc. Nursing students in selected colleges of Punjab. J Multidisciplinary Educational Research. 2022;[volume(issue)]:[page numbers].
- Roediger HL, Karpicke JD. Test-enhanced learning: taking memory tests improves long-term retention. Psychol Sci. 2006;17(3):249-55. doi:10.1111/j.1467-9280.2006.01693.
More Articles
Mr. Devaraj L
RV JOURNAL OF NURSING SCIENCES (RVJNS)
Volume 4 | Isuue 4 | OCTOBER-DECEMBER 2025 | Pages: 1-5
10 October 2025
Ms Kenny Nyokir1, Dr. Mamata N2, Dr. S R Gajendra Singh3
RV JOURNAL OF NURSING SCIENCES (RVJNS)
Volume 4 | Isuue 4 | OCTOBER-DECEMBER 2025 | Pages: 6 - 10
10 October 2025
C.Vinodhini
RV JOURNAL OF NURSING SCIENCES (RVJNS)
Volume 4 | Isuue 4 | OCTOBER-DECEMBER 2025 | Pages: 11-14
10 October 2025

Ms. Viyana Lima1, Ms. Tasmia Balbatti2, Ms. Vaishnavi Wanjole3, Mr. Vivekrao Hosure4, Mr. Yashavant Pawar5 and Mr. Kiran Savaganve6.
RV JOURNAL OF NURSING SCIENCES (RVJNS)
Volume 4 | Isuue 4 | OCTOBER-DECEMBER 2025 | Pages: 15-20
10 October 2025
M.Priyadharsini
RV JOURNAL OF NURSING SCIENCES (RVJNS)
Volume 4 | Isuue 4 | OCTOBER-DECEMBER 2025 | Pages: 21-23
10 October 2025
Dr. Basavaraju G1, Mrs. Bhagyavathi2
RV JOURNAL OF NURSING SCIENCES (RVJNS)
Volume 4 | Isuue 4 | OCTOBER-DECEMBER 2025 | Pages: 24-27
10 October 2025

Chandana Devi1, Prof Poornima2, Dr Laishram Dabashini Devi3
RV JOURNAL OF NURSING SCIENCES (RVJNS)
Volume 4 | Isuue 4 | OCTOBER-DECEMBER 2025 | Pages: 28-34
10 October 2025